"The Science Behind Mobile Communication: How It All Works"
The Science Behind Portable Correspondence: How Everything Works
In the present hyper-associated world, portable correspondence has turned into a key piece of our lives. Whether it's talking with friends and family, leading conferences, or streaming our number one shows, the innovation empowering this consistent correspondence is a wonder of current science. Be that as it may, have you at any point considered how versatile correspondence really functions? We should plunge into the entrancing science behind it.
The Nuts and Bolts of Portable Correspondence
At its center, versatile correspondence is the trading of voice, text, or information between gadgets utilizing remote innovation. Dissimilar to conventional media transmission frameworks that depend on wired associations, portable correspondence uses electromagnetic waves to communicate data over tremendous distances.
This remote correspondence is made conceivable by:
Radio Waves: These are the underpinning of versatile correspondence, going about as transporters for information transmission.
Cell Organization: A portable correspondence framework is worked around an organization of interconnected cells, each with its own base station.
Cell Phones: Cell phones, tablets, and other portable empowered gadgets convey and get messages from these organizations.
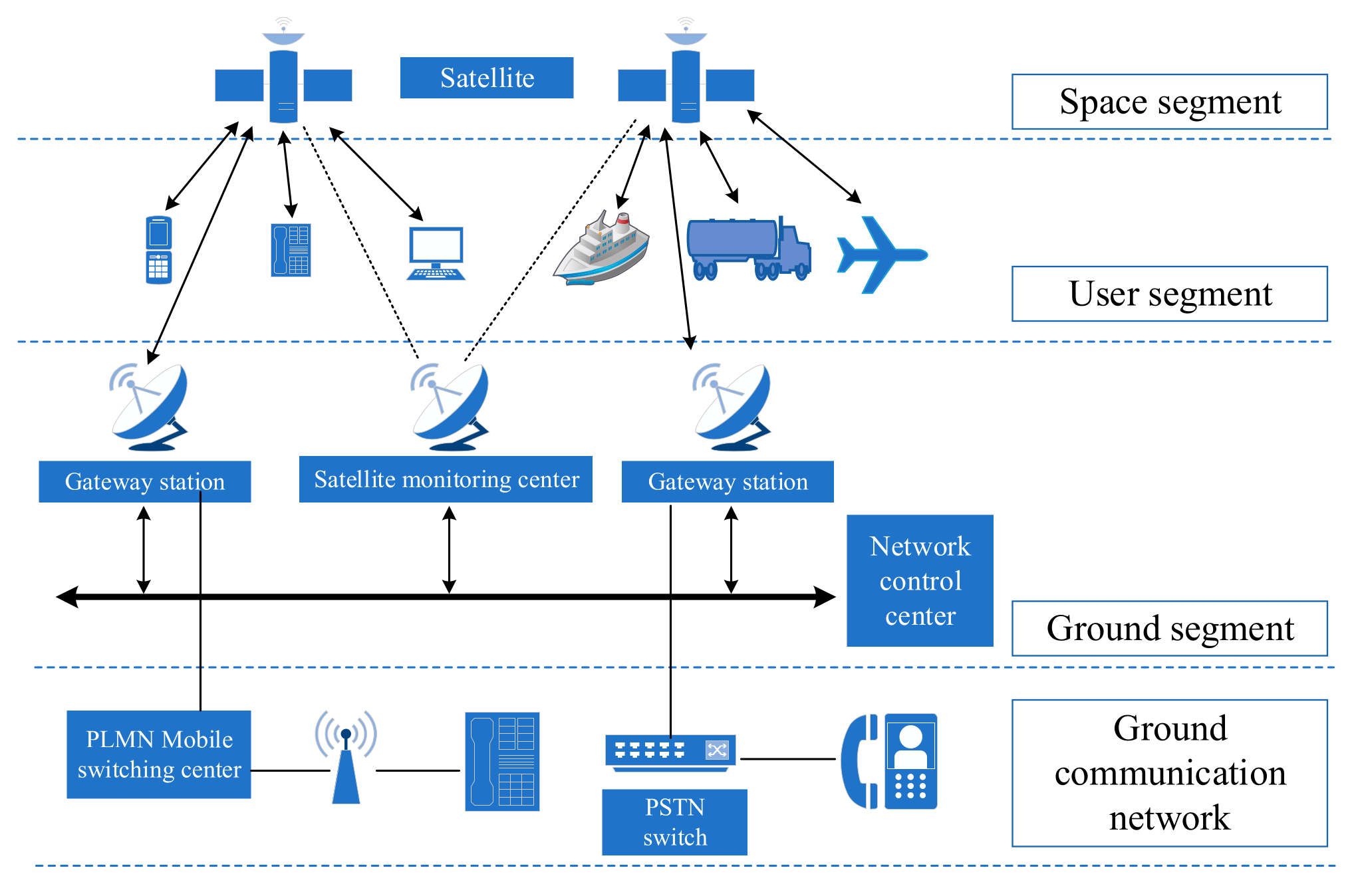
The Cell Organization Framework
The expression "cell" comes from the division of topographical regions into little segments called cells. Every cell is outfitted with a base station that comprises of a pinnacle and recieving wires. This organization structure guarantees proficient inclusion and asset use.
1. Base Stations and Cells
A base station goes about as the correspondence center point for a particular cell, interfacing cell phones inside its reach to the organization.
These cells are intended to cover somewhat, permitting consistent handovers when a gadget moves starting with one cell then onto the next.
2. Frequencies and Channels
Portable correspondence depends on unambiguous recurrence groups distributed by administrative specialists.
Every phone works on a novel recurrence reach to keep away from impedance with adjoining cells.
3. Center Organization
The center organization associates base stations to the more extensive broadcast communications foundation and the web. It oversees fundamental undertakings, for example:
Steering calls and information
Confirming clients
Charging and supporter the board
How Portable Correspondence Functions
The course of portable correspondence includes a few stages, consistently coordinated to guarantee ongoing network:
1. Signal Transmission
At the point when you settle on a decision or communicate something specific, your gadget changes over the sound or text into computerized signals.
These signs are sent as electromagnetic waves to the closest base station.
2. Signal Handling
The base station processes the got signals and advances them to the center organization.
For voice calls, the signs are shipped off the Public Exchanged Phone Organization (PSTN).
For web based correspondence, they are directed through the web.
3. Signal Gathering
The beneficiary's gadget gets the sent signs from its closest base station.
The gadget translates the signs, changing over them back into sound, text, or information.
This whole cycle occurs in simple milliseconds, empowering ongoing correspondence.
The Job of Radio Waves
Radio waves are the foundation of versatile correspondence. They have a place with the electromagnetic range and are utilized to bring data through the air. Key qualities of radio waves include:
Recurrence: Decides the speed and limit of information transmission. Higher frequencies (e.g., 5G) permit quicker information rates yet have more limited range.
Frequency: Conversely connected with recurrence; lower frequencies have longer frequencies, empowering better entrance through snags.
Versatile correspondence fundamentally utilizes microwave and millimeter-wave frequencies, which equilibrium reach and information limit successfully.
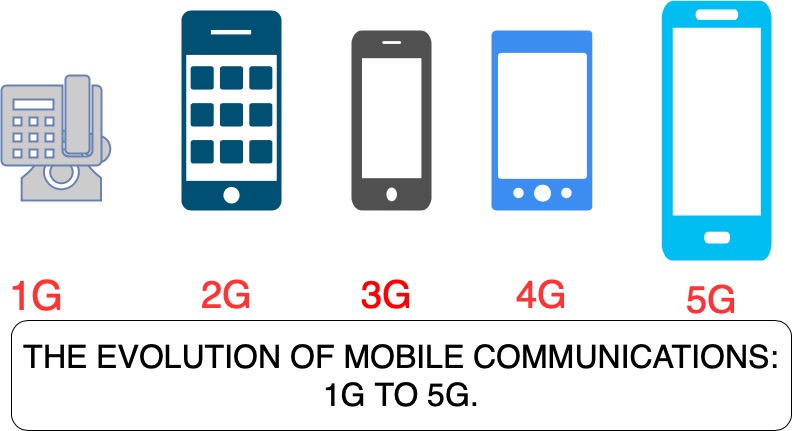
Ages of Versatile Correspondence
The development of versatile correspondence is set apart by the presentation of progressive ages (G) of innovation, each offering critical headways:
1. 1G: Simple Voice
Presented during the 1980s, 1G involved simple signs for voice correspondence.
Restricted inclusion and unfortunate call quality were its significant downsides.
2. 2G: Advanced Voice and SMS
Sent off during the 1990s, 2G denoted the shift to advanced innovation.
Empowered administrations like text informing (SMS) and better call quality.
3. 3G: Portable Information
The mid 2000s saw the ascent of 3G, empowering quicker information velocities and portable web.
It made ready for applications, video calls, and media informing.
4. 4G: High velocity Broadband
4G carried broadband-like velocities to cell phones, changing the manner in which we consume content.
Advancements like LTE (Long haul Development) offered improved network and low inertness.
5. 5G: What's to come is Here
The most recent age, 5G, offers super high velocities, negligible inactivity, and backing for enormous gadget network.
It is driving advancements like independent vehicles, shrewd urban areas, and increased reality.
Advances Driving Versatile Correspondence
A few advances work pair to make versatile correspondence conceivable:
1. Balance
Adjustment is the method involved with encoding data onto transporter waves. Normal strategies include:
Sufficiency Balance (AM)
Recurrence Balance (FM)
Stage Balance (PM)
2. Various Access
To permit various clients to have a similar recurrence band, portable organizations use:
Time Division Numerous Entrance (TDMA): Partitions time into openings for every client.
Recurrence Division Various Access (FDMA): Distributes separate frequencies for clients.
Code Division Different Access (CDMA): Appoints exceptional codes to clients.
Symmetrical Recurrence Division Different Access (OFDMA): Divides frequencies into more modest sub-transporters for proficient use.
3. Recieving wires and MIMO
Current organizations utilize numerous information, different result (MIMO) radio wires to improve information throughput and dependability by communicating various information streams at the same time.
Challenges in Portable Correspondence
Regardless of its exceptional capacities, versatile correspondence faces a few difficulties:
1. Impedance
Signals from different sources can impede one another, debasing quality.
2. Inclusion Issues
Provincial and distant regions frequently need adequate foundation, prompting network holes.
3. Range Shortage
With the developing interest for versatile administrations, the accessibility of recurrence groups is restricted.
4. Security and Protection
Safeguarding client information and forestalling unapproved access stay basic worries.
The Fate of Portable Correspondence
The excursion of portable correspondence is not even close to finished. Arising innovations guarantee considerably more prominent progressions:
6G Organizations: Expected to present paces to multiple times quicker than 5G, empowering genuinely vivid encounters.
Artificial intelligence and AI: Upgrading network the executives, prescient support, and client encounters.
Quantum Correspondence: Giving extraordinary security to information transmission.
Satellite-Based Portable Organizations: Crossing over network holes in distant regions.
End
The science behind versatile correspondence is a demonstration of human resourcefulness and development. From the beginning of simple telephones to the appearance of 5G and then some, this innovation has changed how we associate and collaborate. By understanding the standards and cycles that drive versatile correspondence, we can more readily value the fantastic frameworks that keep us associated in an undeniably advanced world.