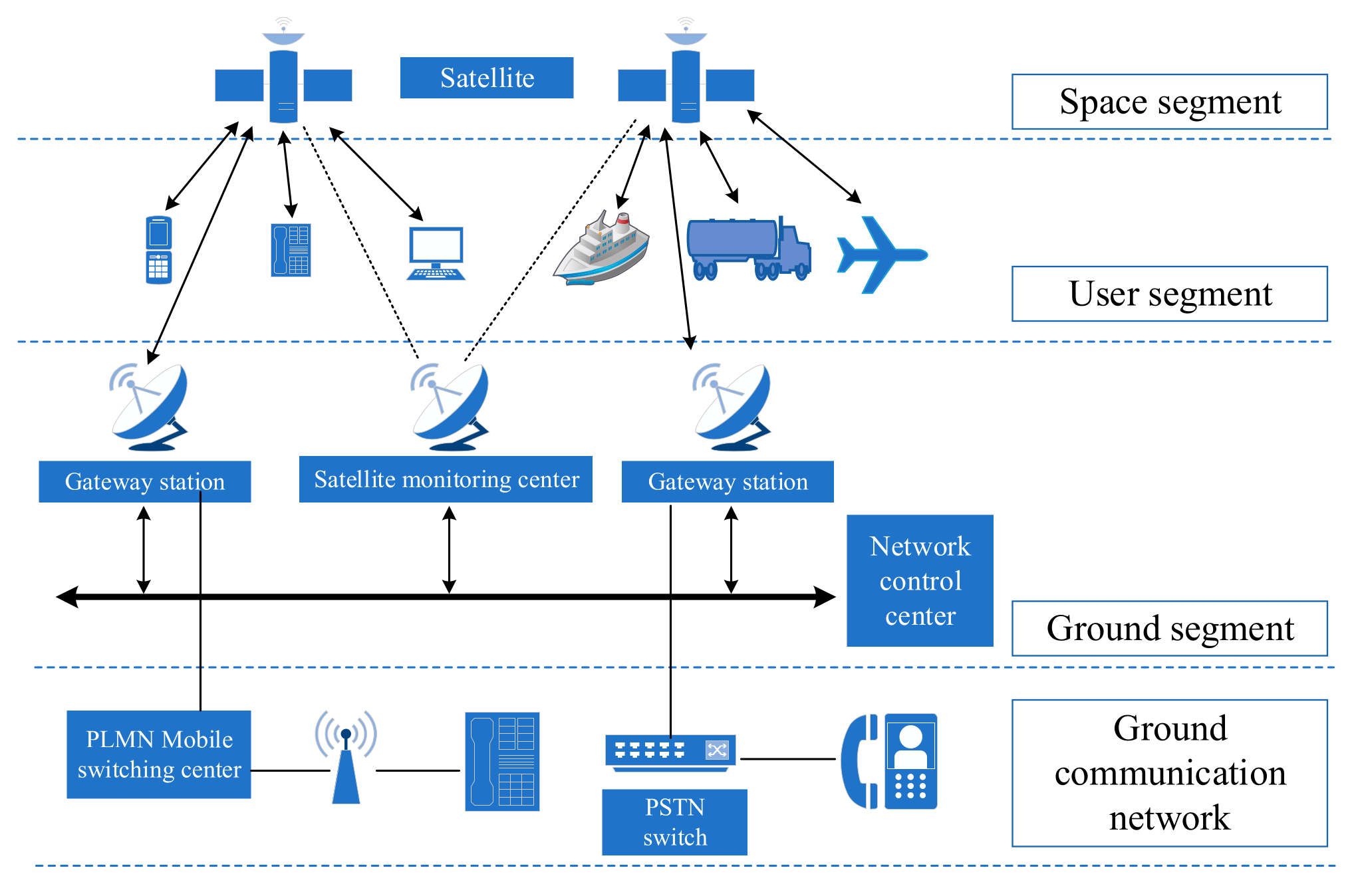
"From 1G to 5G: The Journey of Mobile Connectivity"
The development of portable networks, traversing from the simple 1G organizations to the present fast 5G frameworks, recounts an entrancing story of mechanical advancement and cultural change. Versatile organizations have not only reformed how we impart but have also assumed a crucial part in forming economies, businesses, and societies around the world. This article dives into the achievements of portable networks, investigating the key attributes, accomplishments, and effects of every age.
1G: The Introduction of Portable Correspondence
The original (1G) of portable organizations denoted the approach of remote correspondence. Presented in the last part of the 1970s and mid-1980s, 1G organizations depended on simple innovation to communicate voice signals. The High-level Cell Phone Framework (AMPS), created in the US, became perhaps the earliest financially sent 1G framework.
Key Elements of 1G:
Simple Innovation: Voice signals were sent as nonstop waves, making it inclined to impedance and low quality.
Restricted Inclusion: Base stations had restricted ranges, and network was sketchy in rustic regions.
Massive Gadgets: Early cell phones, for example, the famous Motorola DynaTAC, were huge, weighty, and costly.
In spite of its limits, 1G was notable. It acquainted the world with the idea of portable communication, empowering voice correspondence in a hurry. Be that as it may, the simple idea of 1G organizations made them helpless against listening in and offered no help for information transmission.
2G: The Computerized Transformation
The progress to second-age (2G) networks in the mid-1990s brought huge headways, including the shift from simple to advanced innovation. This change further improved call quality, increased network capacity, and introduced basic information services.
Key Highlights of 2G:
Computerized Encryption: Improved security for voice correspondence.
SMS and MMS: The presentation of Short Message Administration (SMS) and Media Informing Administration (MMS) changed how individuals conveyed.
Energy Proficiency: Computerized innovation diminished power utilization, broadening battery duration for cell phones.
GSM (Worldwide Framework for Portable Interchanges) turned into the predominant 2G norm, empowering global wandering and normalization. 2G organizations established the groundwork for portable administrations past voice calls, for example, messaging, which immediately acquired prominence around the world.
3G: The Period of Portable Web
The third era (3G) networks, sent off in the mid-2000s, were a unique advantage. With speeds fundamentally quicker than 2G, 3G empowered portable web access, making way for cell phones and application biological systems.
Key Elements of 3G:
High-speed Information Transmission: Paces going from 144 kbps to a few Mbps.
Video Calling: A progressive element enabling face-to-face communication.
Versatile Perusing: Admittance to pages, messages, and mixed media content.
3G organizations upheld new applications, for example, video real-time, portable gaming, and online entertainment stages. The presentation of gadgets like the iPhone exploited 3G's abilities, introducing the cell phone period. Nonetheless, the developing interest for information-heavy applications featured the requirement for considerably quicker networks.
4G: The Time of Fast Availability
The rollout of fourth-age (4G) networks during the 2010s brought uncommon velocities and abilities. In view of advancements like Long-term Evolution (LTE), 4G organizations provided the backbone for modern digital lifestyles.
Key Highlights of 4G:
Blazing Fast Velocities: Download speeds up to 100 Mbps, enabling HD video streaming and seamless browsing.
VoLTE (Voice over LTE): Excellent voice brings over LTE organizations.
Upgraded Availability: Backing for IoT (Web of Things) gadgets and versatile applications.
4G organizations facilitated the growth of video streaming platforms, cloud computing, and high-level portable applications. Administrations like Uber, Netflix, and Instagram flourished in the 4G period, redefining industries and consumer behavior. Nonetheless, as additional gadgets connected to the web, the limitations of 4G in terms of latency and network congestion became clear.
5G: The Next Boondocks
Fifth-generation (5G) networks, first introduced in the late 2010s, represent the pinnacle of mobile connectivity so far. Designed to satisfy the demands of an increasingly connected world, 5G offers groundbreaking capabilities that extend beyond traditional communication.
Key Elements of 5G:
Lightning-Fast Speeds: Peak velocities of up to 10 Gbps, enabling ultra-HD video streaming and rapid downloads.
Low Latency: Latency as low as 1 millisecond, critical for real-time applications like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and autonomous vehicles.
Massive Connectivity: Support for billions of IoT gadgets, paving the way for smart cities and industries.
Energy Efficiency: Advanced energy-saving techniques for sustainable network operations.
5G's transformative potential lies in its ability to enable advancements like remote surgery, smart transportation, and immersive entertainment experiences. By reducing latency and increasing bandwidth, 5G is expected to drive progress in fields like artificial intelligence, robotics, and edge computing.
Cultural and Monetary Impact
The excursion from 1G to 5G has had profound cultural and monetary ramifications. Versatile network has:
Connected Individuals: Bridging geographical and cultural divides through instant communication.
Empowered Organizations: Driving innovation, productivity, and globalization.
Improved Access: Enhancing access to education, healthcare, and information.
Stimulated Economies: Generating trillions of dollars in economic activity and creating millions of jobs.
In any case, this excursion has additionally raised difficulties, for example, the advanced separation, security concerns, and online protection dangers. Resolving these issues stays critical as the world advances to 5G and beyond.
6G : The Road Ahead and Beyond
As 5G organizations keep on expanding, specialists and industry pioneers are already imagining the future: 6G. Expected to emerge during the 2030s, 6G promises to:
Present speeds up to 100 Gbps.
Integrate AI for intelligent network management.
Enable holographic communication and advanced quantum computing.
The future of mobile connectivity will likely blur the lines between the physical and digital worlds, transforming how we live, work, and interact.
Conclusion
The journey from 1G to 5G demonstrates humanity's relentless quest for connectivity and innovation. Each generation of mobile networks has built upon its predecessor, addressing limitations and unlocking new possibilities. As we embrace the 5G era and anticipate the dawn of 6G, the potential for mobile connectivity to transform industries and improve lives remains boundless. The narrative of mobile connectivity is far from finished; it is a testament to the extraordinary power of technology in shaping our world.